I. Introduction
In our rapidly urbanizing world, the environmental impact of building operations has become a crucial concern. Benchmarking Laws and LEED Certification emerge as critical frameworks in addressing these concerns by fostering sustainable architecture. This blog post explores how these regulatory and voluntary measures synergistically promote eco-friendly building practices, highlighting their importance in modern architecture and environmental sustainability.
II. Understanding Benchmarking Laws

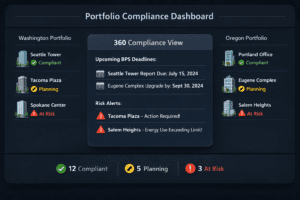
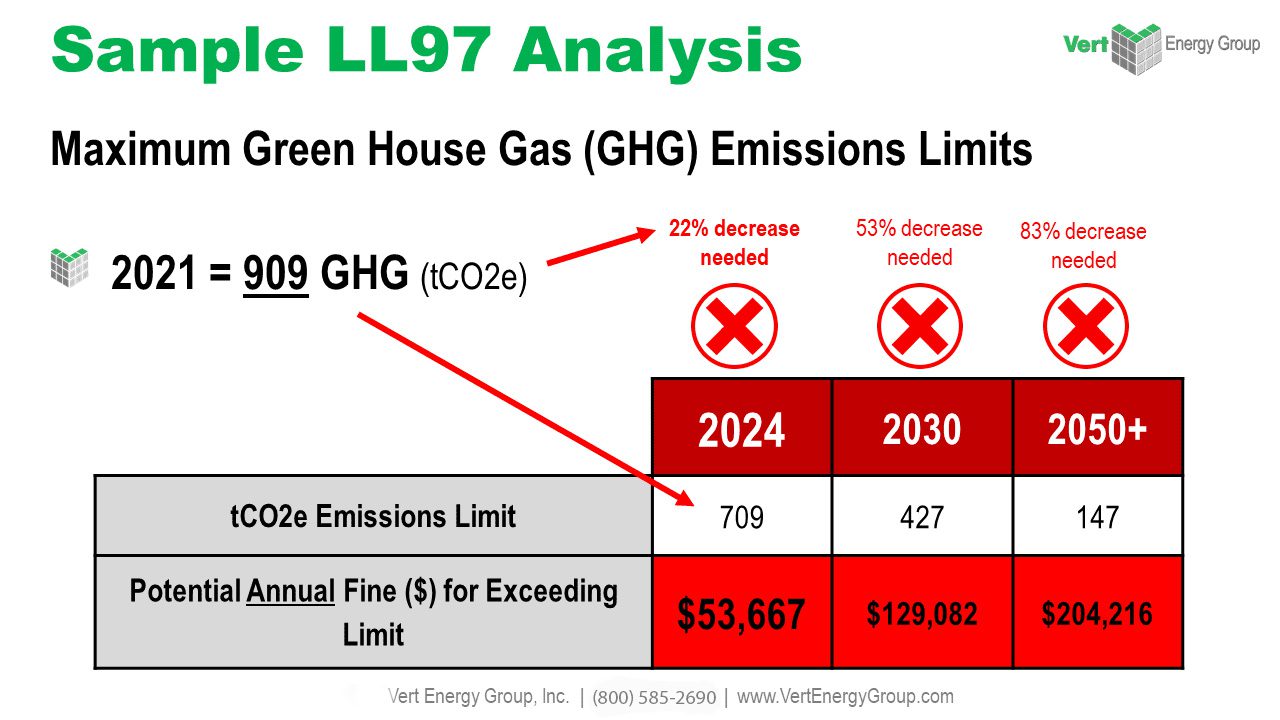
Benchmarking laws mandate that building owners annually measure and publicly report their energy consumption. This practice is aimed at increasing awareness of energy usage and sparking a broader commitment to decrease overall environmental footprints.
Purpose and Benefits
The primary purpose of benchmarking laws is to push the building industry towards greater transparency and accountability in energy usage, which can lead to significant environmental and economic benefits. These laws help identify high-performing buildings and set a performance baseline which can be crucial for setting future efficiency goals. For more details on how benchmarking laws work and their benefits, the Energy Star’s Benchmarking and Energy Performance guide provides a comprehensive look.
Promoting Green Buildings
Through public disclosure of energy usage, benchmarking laws incentivize building owners to adopt newer, more efficient technologies and practices to enhance their competitive edge. Cities like Seattle and Boston have implemented robust benchmarking regulations that have led to widespread improvements in building performance across the board.
III. Understanding LEED Certification
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is an internationally recognized green building certification system. It provides a structured approach to creating environmentally responsible and resource-efficient buildings from construction to operation.
Levels and Process
LEED certification is available in four levels: Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, awarded based on a point system that evaluates aspects such as water efficiency, energy use, and air quality. The process of becoming LEED certified involves registering the project, submitting documentation during and post-construction, and undergoing a review by the Green Building Certification Institute. The U.S. Green Building Council’s official site offers a detailed explanation of the LEED certification process.
Benefits
LEED buildings are designed to be efficient, saving money on electricity, water, and other utilities. They also boast higher lease-up rates and may qualify for a variety of incentives like tax rebates and zoning allowances. LEED-certified buildings contribute positively to the environment and also offer healthier living and working spaces.
IV. The Interplay Between Benchmarking Laws and LEED Certification
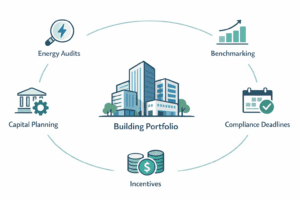
Benchmarking laws and LEED certification complement each other in promoting sustainable building practices. Data collected through benchmarking can highlight areas where a building falls short, providing a clear pathway for LEED projects aimed at enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
Examples of Synergy
In jurisdictions with stringent benchmarking regulations, such as New York City, there is a noticeable trend towards higher LEED certification as building operators seek to improve their reported performance. This has created a dynamic environment where market forces favor greener, more efficient buildings.
V. Role in Promoting Sustainable Buildings
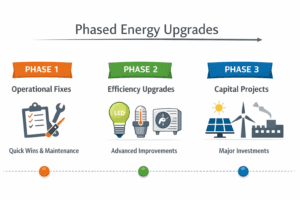
The combined influence of benchmarking laws and LEED certification encourages not only compliance but ambition in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability. They drive innovation in sustainable building design, influencing widespread adoption of green building materials and technologies.
VI. Challenges and Solutions

Despite their benefits, implementing benchmarking laws and achieving LEED certification can be challenging due to costs, complexity, and resistance to change. However, these challenges can be addressed through government incentives, streamlined certification processes, and increased public awareness campaigns. Education plays a crucial role in overcoming barriers, as stakeholders better understand the economic and environmental advantages of sustainable building practices.
VII. Conclusion
Benchmarking laws and LEED certification are indispensable in the push toward sustainable building and construction practices. They not only facilitate but necessitate the adoption of green building materials and strategies, propelling the building industry towards greater environmental responsibility. As urban populations grow, the integration of these practices plays an increasingly vital role in shaping sustainable urban landscapes.
VertPro.com offers tools and services to help property owners and managers improve building energy efficiency and meet regulatory standards. Whether you’re looking for instant pricing on energy audits, need support with benchmark compliance, or want to explore available building upgrade options, VertPro provides user-friendly technology solutions to simplify the process. Their platform helps ensure adherence to over 60 Energy Benchmarking and Efficiency Laws across the country.
For those looking to improve their property’s energy usage and operational value, VertPro.com provides a diverse array of tools and information. The site aims to facilitate a better understanding of energy efficiency practices and legislation, helping building owners and property managers make informed decisions about their energy strategies while complying with all energy ordinances and laws.