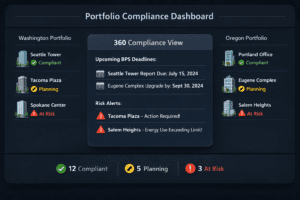
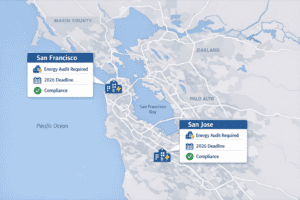
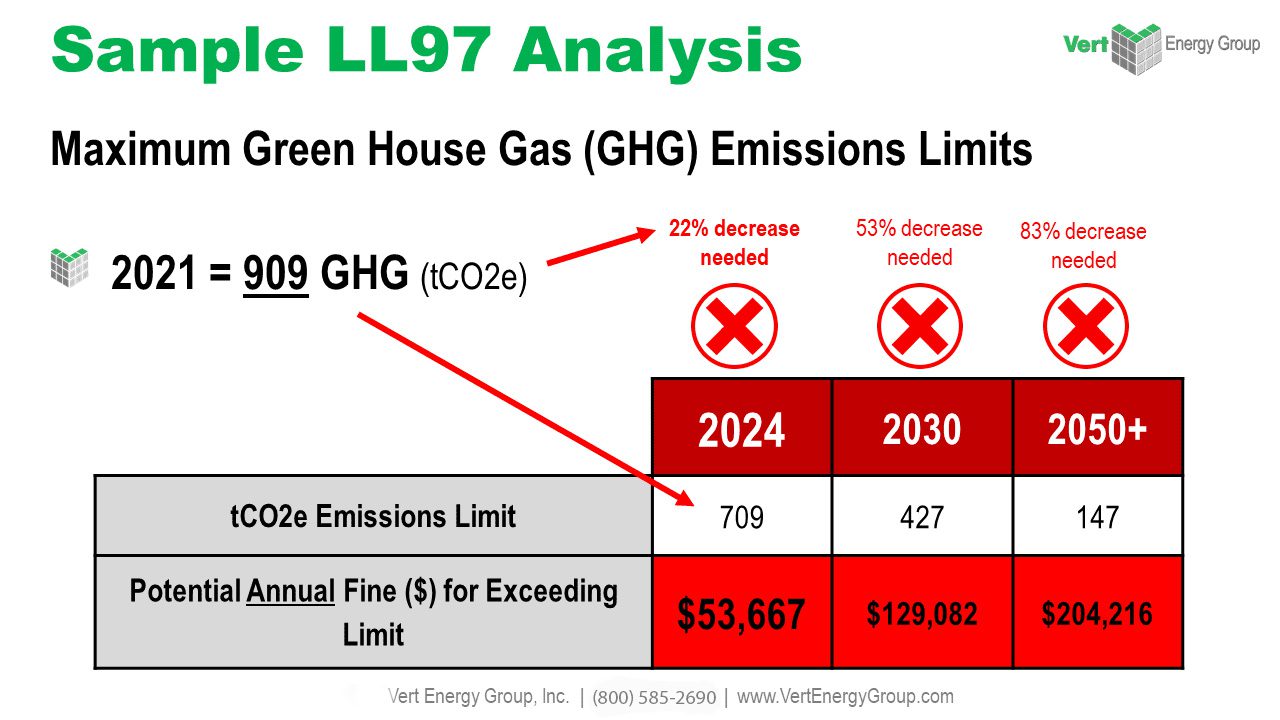
Improving energy performance in commercial buildings isn’t just about sustainability; it’s about increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and maximizing property value. This ENERGY STAR benchmarking case study shows how one building went from a score of 50 to 75 in just twelve months using strategic benchmarking and targeted upgrades.
If you’ve ever wondered what kind of results a strong benchmarking plan can deliver, this real-world success story offers a roadmap worth following.
Starting Point: ENERGY STAR Score of 50
In early 2024, the building owner of a 150,000-square-foot commercial office space approached our team with a clear goal: increase their ENERGY STAR score to improve the building’s marketability and reduce operating costs. Their score at the time, 50, was just average.
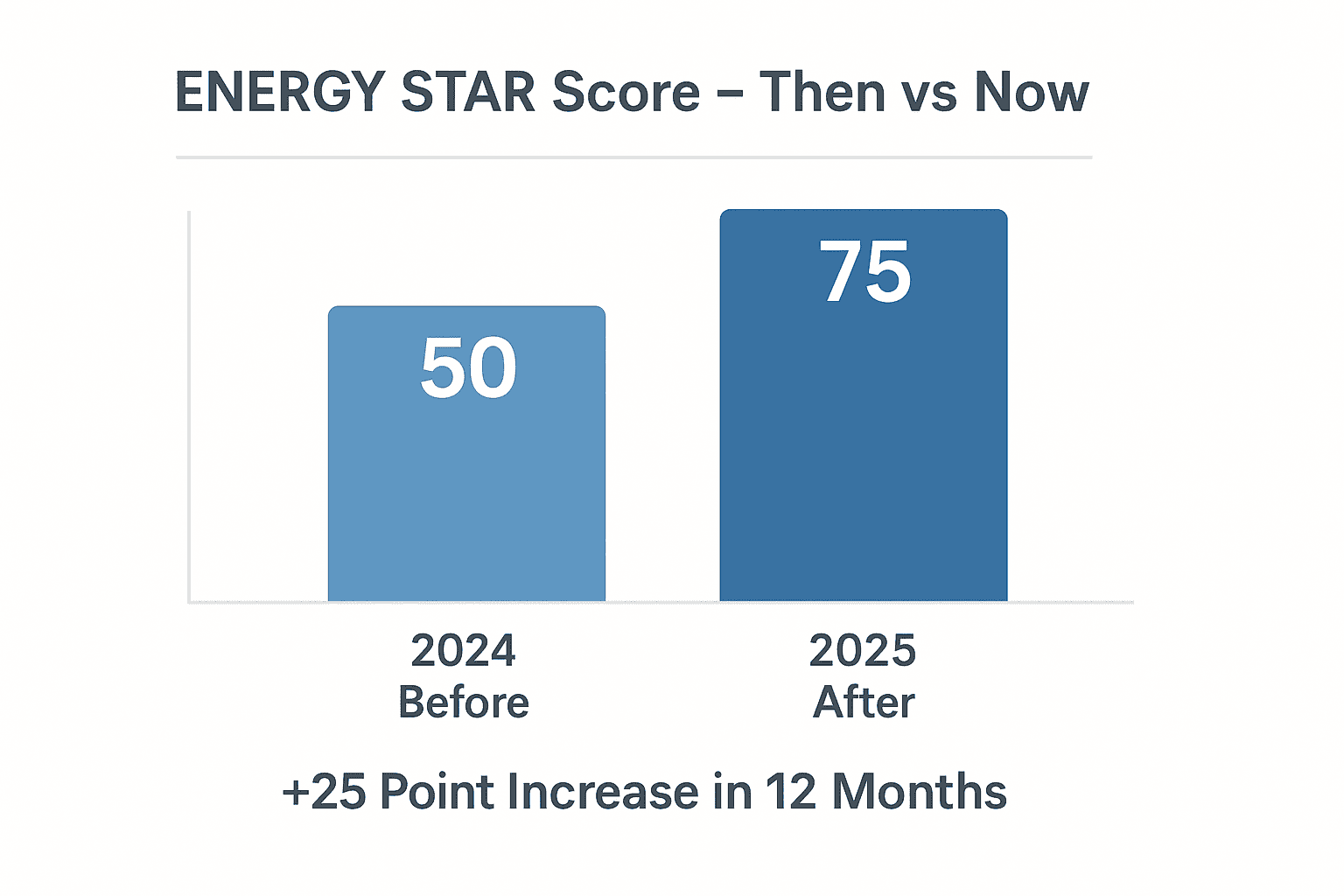
A score of 50 means the building performed better than only half of similar properties nationwide. It wasn’t enough to meet the owner’s goals for tenant retention, sustainability reporting, and operational cost control. They wanted their building to stand out in a competitive market, especially as more cities and tenants started prioritizing ESG criteria.
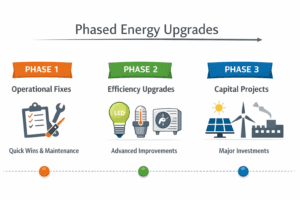
To get there, we launched a 3-phase benchmarking and performance improvement strategy.
Phase 1: Energy Data Collection And Benchmarking
The first step in any successful energy score improvement strategy is data. We conducted a full benchmarking assessment using ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager, which included 12 months of historical energy use data, utility records, and occupancy patterns.
During the benchmarking analysis, we identified several problem areas:
❄️ HVAC systems running during off-hours
💻 Poorly calibrated building controls
💡 Inconsistent lighting controls across tenant spaces
This benchmarking exercise wasn’t just a report—it was the foundation of our improvement strategy. By understanding exactly how and where the building consumed energy, we were able to create a focused action plan for improvement.
Client Quote:
“I thought we were doing fine until I saw the data laid out. Benchmarking showed us the gaps we were missing.” — Building Owner, Midwest Portfolio
Phase 2: Implementing Smart, Low-Cost Upgrades
Not every energy upgrade needs to break the bank. With insights from our benchmarking data, we worked with the building’s operations team to make targeted, cost-effective adjustments.
These Include:
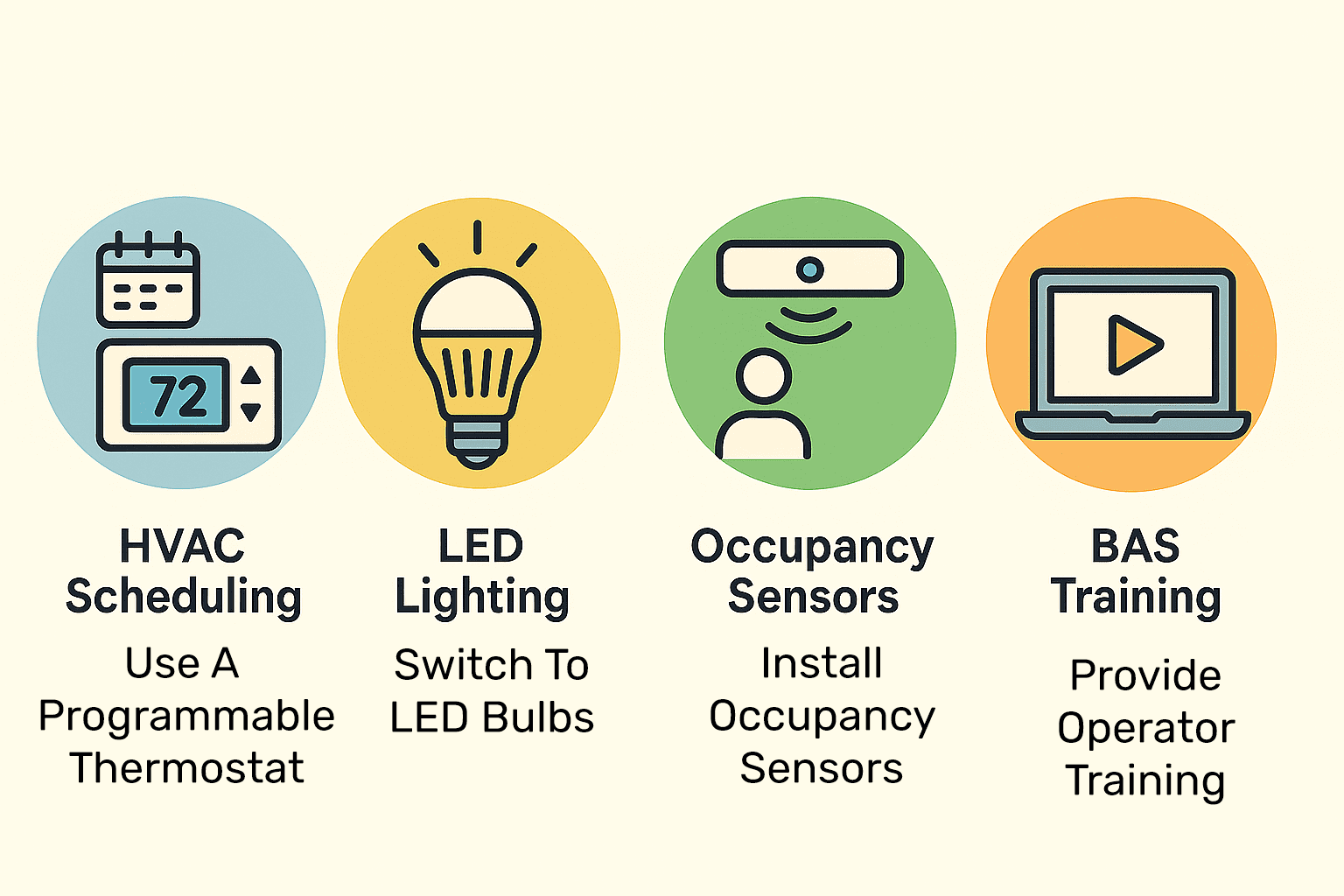
- Reprogramming HVAC schedules to align with actual occupancy
- Installing occupancy sensors in low-traffic areas like restrooms and storage rooms
- Upgrading lighting in common areas to LED, reducing energy use by 18% in those zones
- Training the maintenance team to monitor and adjust building automation systems (BAS) weekly
These changes didn’t require major capital investment, but they generated significant savings. Within four months, energy use dropped 11% compared to the same period the year prior.
Phase 3: Continuous Monitoring And Fine-Tuning

Improvement doesn’t stop with upgrades, it continues through ongoing performance management.
We set up monthly benchmarking check-ins to track the ENERGY STAR score in real time and used interval meter data to identify daily and weekly anomalies. This allowed the team to:
- Quickly respond to spikes in energy use
- Adjust building systems seasonally
- Keep tenant energy use aligned with building-wide goals
The ongoing monitoring kept the building on track for continuous improvement—and by month ten, the ENERGY STAR score hit 75.
Results: ENERGY STAR 50 To 75 In 12 Months
The final results were impressive:
| Metric | Before Benchmarking | After 12 Months |
| ENERGY STAR Score | 50 | 75 |
| Year-over-Year Energy Use | Baseline | -14.7% |
| Estimated Annual Savings | — | $37,500 |
| Tenant Satisfaction Score | 6.8/10 | 8.4/10 |
Improving the building’s ENERGY STAR score by 25 points elevated its competitive standing, attracted new interest from sustainability-conscious tenants, and gave the owner a new tool to leverage for financing and incentive programs.
What You Can Learn From This Benchmarking Success Story
This case study is more than just a feel-good story, it offers tangible takeaways for any building owner looking to improve their commercial energy score.
Here are key lessons:
1: Benchmarking is the blueprint.
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Energy data management through consistent benchmarking is the first step.
2: Targeted upgrades beat big spends.
Start with low-cost, high-impact changes. Lighting and HVAC schedules are often the biggest wins.
3: Ongoing monitoring matters.
A one-time fix is not enough. Performance must be maintained and optimized over time.
4: Higher ENERGY STAR scores create value.
Better scores don’t just lower bills—they improve asset value, financing options, and tenant appeal.
Want To Improve Your ENERGY STAR Score?

If your building has plateaued or underperforms in ENERGY STAR benchmarking, this case study shows it’s possible to make a major leap in just one year. With the right energy data management, team alignment, and performance strategy, real benchmarking improvement is within reach.
Let us help you:
- Identify gaps with a full energy benchmarking report
- Set improvement targets aligned with ESG and financial goals
- Implement smart strategies to raise your score fast
- Track your progress with performance dashboards and expert reviews
Ready To See Similar Results?
Whether your building is at ENERGY STAR 40 or 65, the path to better performance starts with a benchmarking strategy. Let our team help you build your own energy score improvement story, starting today.
Start Your Benchmarking Plan Today »
FAQs
Q: How long does it take to improve an ENERGY STAR score?
A: Most buildings can see measurable improvement within 6–12 months with consistent benchmarking and smart upgrades.
Q: Is ENERGY STAR benchmarking required by law?
A: In many cities, yes. Even where it isn’t mandatory, ENERGY STAR benchmarking is considered best practice for commercial building performance.
Q: What if my building is already efficient?
A: Even high-performing buildings can find 5–10% more efficiency through energy data analysis and system tuning.